When it comes to operating systems, Linux and Windows are two of the most popular choices. While both systems have their own unique features, there are some key differences that set them apart.
Definition of Key Terms
- Kernel: The kernel is the central component of an operating system. It acts as the intermediary between software applications and the computer hardware. The kernel controls the allocation of resources, such as CPU time, memory, and disk space, among other things.
- File Manager: A file manager is a software application used for organizing and manipulating files on a computer. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing and manipulating files, folders, and disks.
- Desktop Environment (DE): A desktop environment is a graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer's operating system. It provides the user with a graphical interface for accessing and managing files, applications, and other resources.
Access to Directories and Processes
In Windows, users have limited control over many directories and processes, as they are protected by the operating system. This means that users do not have the ability to access or modify certain parts of the system.
In Windows, even a software developer has no direct access to the Windows kernel. Access to the kernel is through multiple layers, such as the WinAPI and the WinNTDLL. This means that developers have to work with APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to communicate with the kernel.
Windows users are not able to change the Windows file manager "Explorer.exe". This is because Explorer.exe is a core component of the Windows operating system and cannot be replaced or altered by users.
The same goes for the Desktop Environment (DE) in Windows. Windows users are not able to change the DE that is built into the operating system.
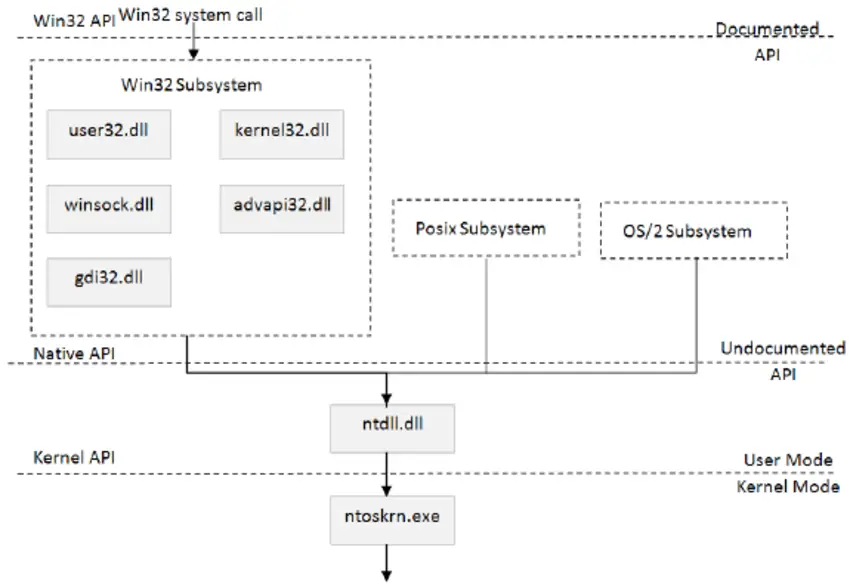
On the other hand, in Linux, users have complete control over the system, including all directories and processes. The superuser account, also known as "root", has complete control over the system, including the ability to modify or delete any part of the system.
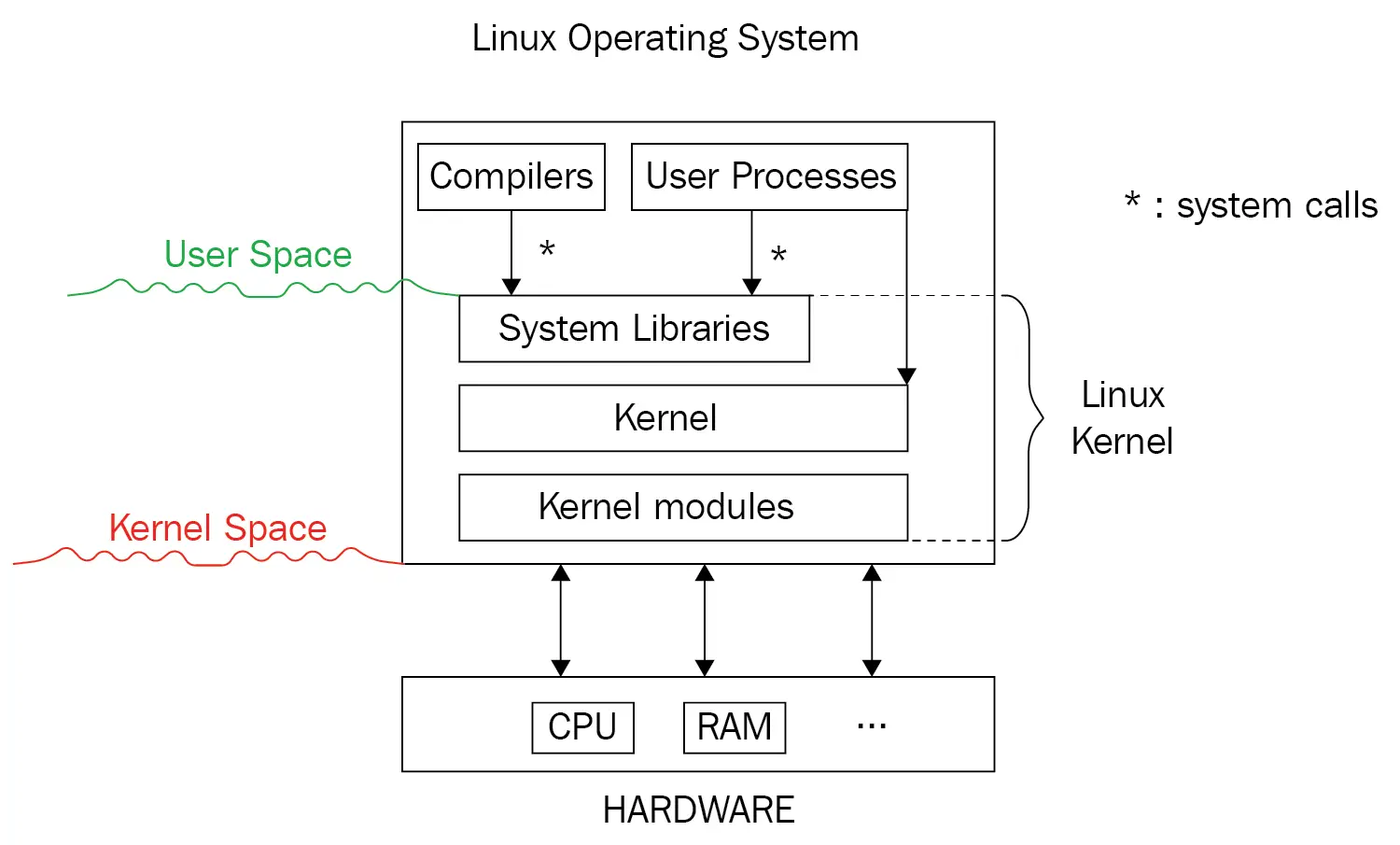
In Linux, system calls go directly to the kernel. This gives Linux developers more control over the system and the ability to directly communicate with the kernel. Linux users have the ability to change both their file manager and DE if they so choose.
This level of customization is one of the key differences between Linux and Windows. Linux offers users more flexibility and control over their computing environment, while Windows provides a more standardized and controlled environment.
This level of control can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. On one hand, it allows users to have complete control over their system and the ability to customize it to their needs. On the other hand, it also means that users have the ability to completely wipe out their system if they are not careful.
Conclusion
These are just some of the differences between Linux and Windows. Both systems have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice for you will depend on your needs and preferences.



















0 Comments, latest